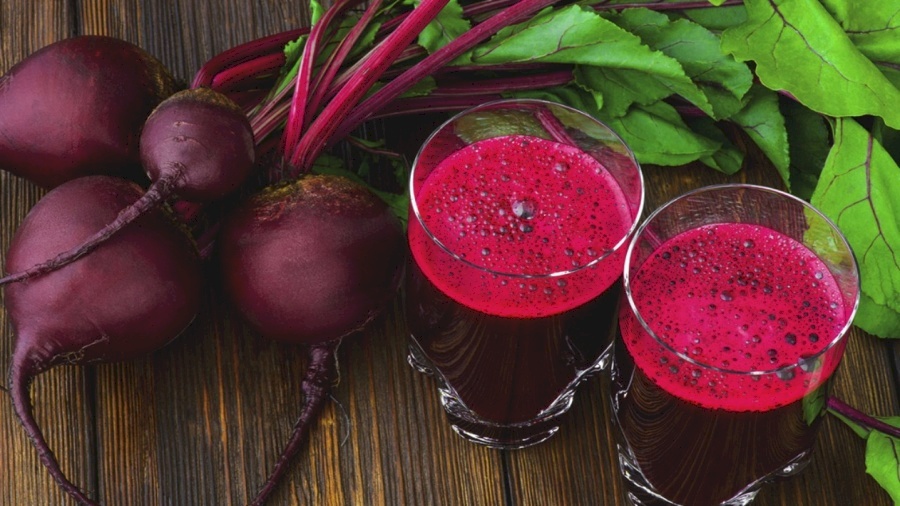

What Happens to Your Blood Pressure When You Regularly Drink Beet Juice?
SadaNews - Beetroot offers numerous health benefits for blood pressure, primarily due to its high levels of nitrates that support cardiovascular health; therefore, regular consumption of beetroot may help lower blood pressure.
Beetroot provides nitrates to dilate blood vessels
Beetroot contains inorganic nitrates (NO3), which your body converts into nitric oxide (NO). This new molecule enhances the relaxation of blood vessels, meaning it dilates the vessels, which provides more space for blood flow, according to the "Verywell Health" website.
Beetroot lowers systolic blood pressure
A review of trials conducted on adults with high blood pressure found that consuming about 200 to 800 milligrams of nitrates through drinking beet juice daily was associated with a reduction in clinical systolic blood pressure by 5.3 millimeters of mercury (the top number in a blood pressure reading that measures the pressure in your arteries when your heart beats and pumps blood out).
Another analysis indicated that beet juice (consuming about 70-250 milliliters daily) significantly reduced systolic blood pressure by an average of 4.95 millimeters of mercury in adults with hypertension.
Beetroot has lesser effects on diastolic blood pressure
Research suggests that the effect of consuming nitrate-rich beetroot may be limited on diastolic blood pressure (the bottom number in a blood pressure reading that measures the pressure exerted by your blood against the walls of your arteries between beats).
In multiple trials, beet juice significantly lowered systolic blood pressure but did not show a statistically significant effect on diastolic blood pressure in some studies.
Results from another analysis indicate that nitrates from beetroot cause a slight decrease in diastolic blood pressure estimated at about 0.9 millimeters of mercury in adults with hypertension. However, this decrease often does not reach a statistically significant level.
Beetroot has an immediate effect
A single dose of beet juice can lower systolic blood pressure by several millimeters of mercury within two to three hours; this leads to a short-term effect resulting from the conversion of dietary nitrates into nitric oxide. There are no indications that regular consumption of beetroot has a prolonged effect on blood pressure for 24 hours.
The short-term effects of consuming beet products depend on individual factors such as age, sex, and baseline blood pressure, with indications that the greater effect may be seen in individuals with high baseline blood pressure and older adults.
Beetroot may sustain long-term effects
A review of current research indicates that the effects of nitric oxide produced from beet juice may support the control and management of arterial hypertension for up to two months, provided nitrate intake is maintained during this period.
Upon stopping regular dietary nitrate intake, levels of nitrates and nitrites tend to return to previous levels; this suggests that the benefits of beetroot on blood pressure depend on continuous consumption, according to available research.
Studies indicate that regular consumption of beetroot for two weeks may help achieve sustainable results and assess its effects on blood pressure.
Side effects
Some research has pointed out that the effect of nitric oxide resulting from beetroot consumption may not be consistent in patients taking antihypertensive medications.
Evidence from studies on the effects of consuming beet products suggests that it should be combined with other lifestyle strategies for managing blood pressure rather than used as a sole treatment, and it is advisable to consult a physician regarding drinking beet juice, especially if you are taking medications for high blood pressure.

Amazon Web Services Faces Power and Connectivity Issues in the UAE and Bahrain

Dual Sleep Disorders Increase Heart Burden

Fasting and Exercise: A Delicate Balance Between Enthusiasm and Health

From Football to Cycling and Skiing.. Turkey's Plan to Expand Sports Tourism

Russian Regulator Demanded Telegram to Remove 35,600 Harmful Content Since the Start of th...
Scientists Attempt to "Intercept Cancer" Before Its Formation.. Know the Details

American Fact-Checking Platform Exposes Trump's Exaggerations in State of the Union Addres...

