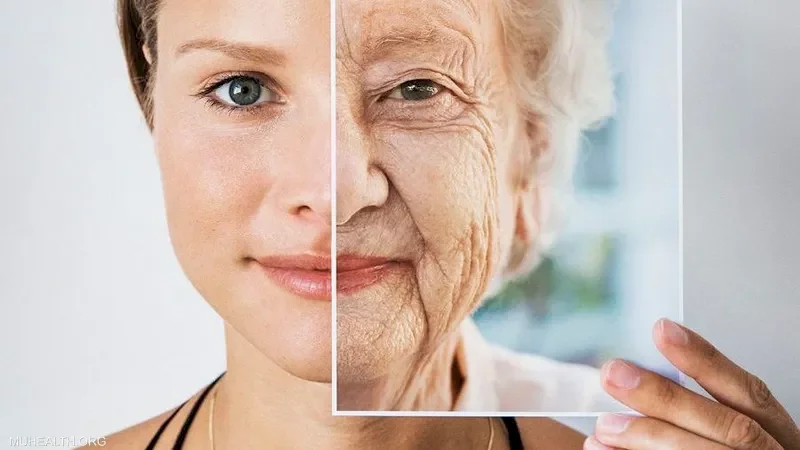

Extreme Heat Accelerates Aging
SadaNews - Everyone feels the fatigue and dehydration resulting from spending a long time in the heat, but research shows that the effects of exposure to extreme heat go beyond heatwaves; prolonged exposure to high temperatures can accelerate the aging of the body.
A new study has found that repeated exposure to heatwaves is associated with accelerated aging and increases the likelihood of health problems.
According to what was published by the American magazine "Time" quoting the journal Nature Climate Change, the more intense the heatwaves an individual is exposed to, the more aging occurs in their body.
Over 16 Years
Researchers analyzed medical data for nearly 25,000 individuals in Taiwan over 16 years, specifically between 2008 and 2022, during which the region experienced 30 heatwaves (defined by researchers as "a period of elevated temperature over several days").
The researchers were also able to calculate a person's biological age using the results of numerous medical examinations, including assessments of liver, lung, and kidney functions, blood pressure, and inflammation levels.
They then used the participants’ addresses in the two years prior to their medical visit to compare their biological ages to the temperatures they were likely exposed to.
Speeding Up Aging
The researchers discovered that the more intense the heat exposure a person faced, the faster their aging process was, where every additional 1.3 degrees Celsius of cumulative heat added between 8 to 12 days to their biological age.
Significant Public Health Implications
Kway Kuo, the lead researcher of the study and an environmental epidemiologist at the University of Hong Kong, stated to Nature that "while the number itself may seem small, over time and across populations, this effect can have significant implications for public health."
Combating Extreme Heat
Climate change is increasing the prevalence of extreme heatwaves globally. The year 2024 has been the hottest year on record, surpassing the record set in 2023. Results from a study conducted by the Climate Center revealed that 88% of 247 major U.S. cities have experienced an increase in the number of extremely hot days since 1970.
Climate models indicate that global temperatures will continue to rise, with the World Meteorological Organization estimating a 70% likelihood that the average warming over five years (2025-2029) will exceed 1.5 degrees Celsius. Experts emphasize that finding solutions to combat extreme heat will become increasingly urgent as temperatures rise.
Scientists Attempt to "Intercept Cancer" Before Its Formation.. Know the Details

American Fact-Checking Platform Exposes Trump's Exaggerations in State of the Union Addres...

How Mourinho Deceived Everyone and Watched the Match Between Real Madrid and Benfica from...

Fat Loss Improves Blood Pressure and Supports Immunity

Galaxy S26 Armed with a Smart Feature to Combat the Most Dangerous Threats to Smartphones
Discovery of Microplastic Particles in 90% of Prostate Cancer Cases

Artificial Intelligence Diagnoses Children's Brain Tumors with 92% Accuracy Without Surger...

