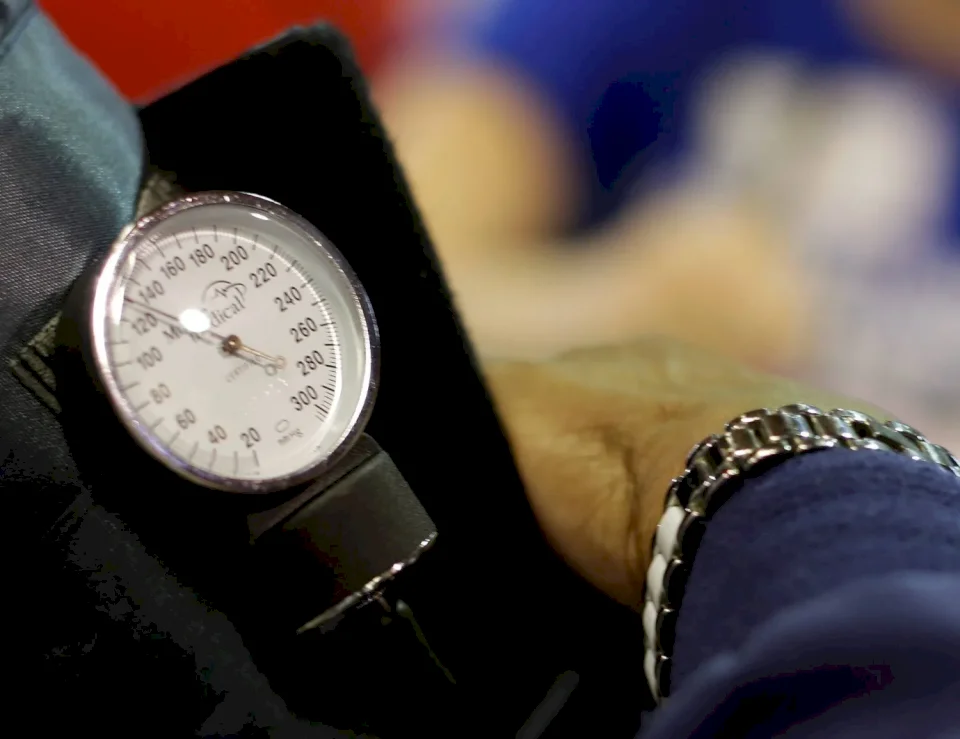

New Updates to Hypertension Treatment Protocol
SadaNews - Nearly half of adults in the United States suffer from high blood pressure, which is one of the most significant preventable risk factors associated with heart disease, stroke, heart attacks, heart failure, kidney disease, and even dementia.
For the first time since 2017, the American Heart Association and the American College of Cardiology have updated their guidelines to help those with hypertension better manage their levels, based on a growing body of new scientific evidence.
Dr. Daniel W. Jones, chair of the guidelines writing committee and Dean and Professor Emeritus at the University of Mississippi Medical Center, stated that the new updates reflect new evidence that provides people with better opportunities for longer, healthier lives.
Stability of Core Definitions
Despite the updates, the new guidelines have kept the definitions of blood pressure unchanged, as follows:
Blood pressure is considered normal if it is less than 120/80 mmHg
Elevated if it ranges from 120 to 129/80
Hypertensive if it is 130/80 or higher
6 Key Recommendations
The new guidelines focused on 6 essential steps for managing high blood pressure:
1- Starting Medication Early
The guidelines recommend prescribing medications earlier, especially if lifestyle changes over 3 to 6 months do not lead to significant improvement. This is due, according to experts, to increasing evidence linking high blood pressure to cognitive decline.
2- Further Reducing Sodium Intake
The guidelines advise limiting sodium intake to less than 2300 mg per day, aiming for 1500 mg. Reducing salt, even slightly, is an effective step to improve heart health and lower blood pressure.
3- Limiting or Abstaining from Alcohol
The guidelines encourage abstaining from alcohol or limiting to one drink daily for women and two drinks for men, after studies showed that alcohol consumption gradually raises blood pressure over time.
4- Managing Stress and Engaging in Physical Activity
Chronic stress is linked to heart disease, so the guidelines recommend exercising and incorporating relaxation techniques such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing, along with 75–150 minutes of physical activity weekly.
5- Weight Loss
The guidelines stress the importance of losing at least 5% of body weight for those who are overweight or obese, as weight loss is one of the most effective means of lowering blood pressure and reducing its complications.
6- Following the DASH Diet
The guidelines continue to recommend the DASH (Dietary Approaches to Stop Hypertension) diet, which focuses on reducing salt and increasing the intake of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, and low-fat dairy products, due to its proven impact on lowering blood pressure.
The Importance of Monitoring Readings
Cardiologists emphasize the necessity of regularly monitoring blood pressure, whether in clinics or using home monitoring devices, and sharing readings with the doctor to assess the need for lifestyle changes or medication adjustments.
Doctors agree that managing blood pressure remains one of the most important keys to preventing cardiovascular diseases, stressing not to change any treatment plan or stop medications without consultation.
Source: Websites

New Updates to Hypertension Treatment Protocol

A New Comet Ignites Astronomers' Enthusiasm as They Await Its Survival from the Sun's Flam...
8 Daily Habits That Harm Your Heart Health.. How to Avoid Them?

Interactive Digital Photo Frame... Suited to Your Personality and Environment

Women or Men... Who Views Artificial Intelligence as More Dangerous?

120,000 Ready to Assist Him... Artificial Intelligence Employs Humans to Perform Tasks It...

Study: The Keto Diet Improves Symptoms of Treatment-Resistant Depression

