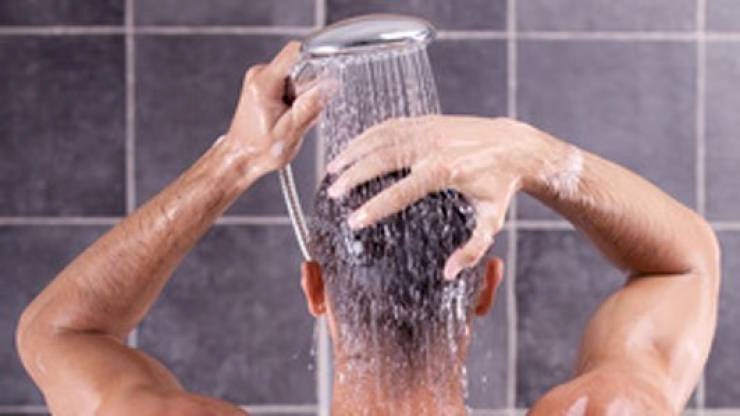
The Trend of ‘Bathing in the Dark’... Does It Really Help for Better Sleep?
SadaNews - If you find it difficult to fall asleep, you may have come across a new and relatively strange trend on social media known as "bathing in the dark."
This trend involves bathing with dim lighting, or turning off the lights completely, often as part of a nighttime routine to relax before sleep.
According to a report published by Healthline, supporters of this method on social media platforms assert that it helps calm the mind, reduce stress, and even improve the quality of sleep.
Unlike morning showers, which are usually used to energize and wake the body, "bathing in the dark" aims to minimize light exposure, regulate body temperature, and enhance relaxation in preparation for sleep.
But does bathing in the dark actually help you fall asleep faster or deeper? Or is it just a comforting ritual that provides a nice feeling at the end of a long day? This is what experts clarify.
Does "bathing in the dark" improve sleep quality?
Chelsea Rohrschreib, a neuroscientist and sleep expert, and head of sleep research at "Wesper," said that bathing in the dark may prepare the brain and body for sleep, which speeds up the time it takes to fall asleep and generally improves its quality.
She explained that the brain requires a slight drop in core body temperature, usually by about one degree, to initiate the sleep process.
She added: "Bathing in warm water quickly raises body temperature, then the core temperature drops quickly after exiting the bath, which mimics the natural process that occurs in our bodies before sleep, making it easier for the brain to transition into sleep state."
Moreover, bathing in the dark limits light exposure in the evening, supporting the body's natural biological clock and signaling that it is time to relax.
Chelsea Rohrschreib noted that the hormone "melatonin," which regulates the sleep-wake rhythm, is affected by the light that enters our eyes; constant exposure to light suppresses its production, while low lighting helps increase it. Thus, bathing with the lights off enhances melatonin secretion and prepares the brain for sleep in advance.
Does it have mental health benefits?
Beyond improving sleep, "bathing in the dark" may also provide psychological benefits.
Chelsea Rohrschreib noted that it is a good way to relax and reduce stress before sleep, as it helps shift the nervous system into the state responsible for comfort and drowsiness, which also contributes to lowering levels of the hormone "cortisol," linked to wakefulness and stress.
For her part, Patricia Reed, a sleep coach at "Goldilocks Sleep Solutions," sees that bathing in the dark can turn into a mindful meditative practice.
She said: "In the dark, we give our other senses more space to work, allowing us to focus on the soothing sensation of warm water on our bodies, the fragrant smells of our soaps, and the gentle sound of flowing water."
She added that this atmosphere resembles a state of meditation, where thoughts and worries can be envisioned drifting away with the water, preparing a fresh mental page for receiving sleep, then starting the next day with more energy.
Not a magical solution for sleep problems
The good news is that experts do not see any obvious harms in this method, but they warn against considering it a quick fix for sleep problems.
People who suffer from chronic sleep disorders or underlying medical conditions may not find significant benefit without specialized medical intervention.
Patricia Reed also emphasized the importance of mindset; if a person treats "bathing in the dark" as a magical solution, they may not reap the expected benefits. If the bath is taken quickly just for cleanliness, the benefits of relaxation and stress reduction will be lost.
She cautioned against considering it an additional task on the daily to-do list, as the pressure to accomplish it may yield counterproductive results and increase stress instead of reducing it.
Scientifically Proven Strategies for Improving Sleep
Apart from this trend, there are proven practices that can help achieve better sleep:
- Stick to a regular sleep schedule by going to bed and waking up at approximately the same time each day, including weekends.
- Avoid caffeine at least six hours before sleep, as some of it can remain active in the body for a long time and affect the ability to sleep.
- Stay away from heavy or hard-to-digest meals about three hours before sleep.
- Avoid bright lights before sleep, especially overhead lighting and screens from electronic devices.
- Keep the bedroom dark, cool, quiet, and comfortable.
Experts recommend that if you cannot sleep after about 20 minutes of lying down, it is better to get up and do a calming activity in dim lighting, such as listening to soft music for a short period, then return to bed and try again.

How to Recover Your Lost Data?

Artificial Intelligence Takes Over the Internet... and Personal Data

How Does "Valentine's Day" Become a Real Test for Artificial Intelligence in Understanding...

Mimicking "Ozempic"... How effective are patches that promise easy weight loss?

Everyday Foods Filled with Microplastic Particles

The Trend of ‘Bathing in the Dark’... Does It Really Help for Better Sleep?

Common Houseplant May Be Key to Alzheimer's Combat