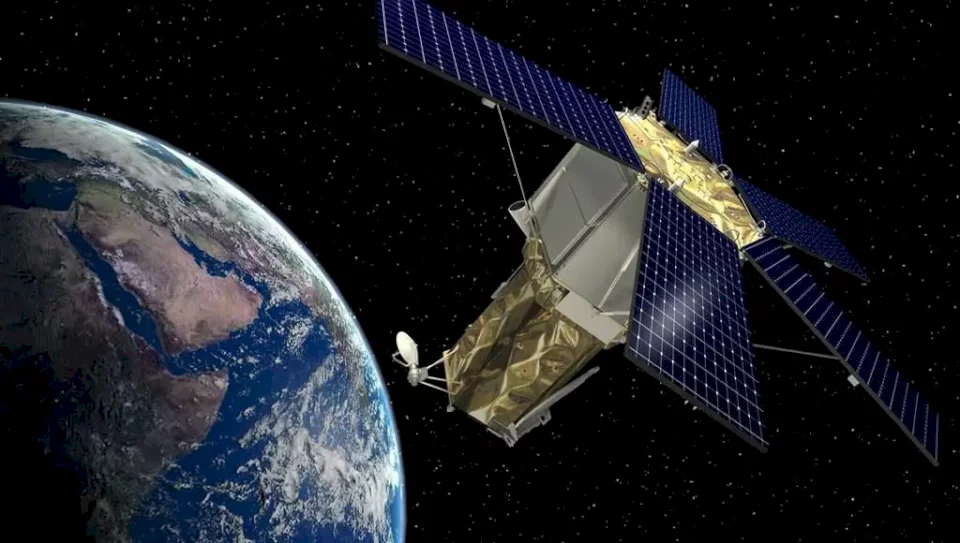

6G Research Transforms Satellites into Edge Computing Hubs
SadaNews - As the global race towards 6G networks accelerates, it seems that the real battleground may not be on Earth, but in space.
While the commercialization of 6G is expected by 2030, researchers have already begun reimagining how artificial intelligence can operate on a global scale.
The International Telecommunication Union (ITU) has identified a series of future use cases for 6G networks, prominently including "deep integration of artificial intelligence and communications" and "ubiquitous connectivity everywhere," signaling a shift from mere data transmission to intelligent platforms capable of processing and decision-making, according to a report published by "interestingengineering" which was reviewed by "Al Arabiya Business".
However, the biggest challenge remains providing seamless AI services to remote areas lacking infrastructure, especially with increasing processing loads and time-sensitive applications.
Satellites Enter the AI Lineup
A new study presented by researchers from the University of Hong Kong and Xidian University proposes a solution that transcends ground-based networks by integrating edge AI with a combined space-ground network, transforming satellites into centers for communication and computing simultaneously.
This approach, dubbed "liquid AI between space and Earth," leverages the movement of satellites themselves to overcome persistent issues that have hindered the use of AI in orbit, such as limited motion speed and bandwidth between space and Earth.
AI Flowing Like Water
The researchers drew inspiration from the seamless flow of water across boundaries, as the new framework allows for the continuous transfer of AI models and data between satellites and ground stations.
This concept is based on three key technologies:
Liquid Learning:
Aims to reduce model training time through a federated learning approach that does not rely on complex infrastructure.
Instead of viewing satellite movement as a barrier, it is exploited to disseminate model parameters and blend them across different regions, accelerating the achievement of more accurate results.
Liquid Inference:
Focuses on enhancing real-time AI decision-making by partitioning neural networks into sub-models distributed between space and Earth, allowing adaptation to available resources and connection quality while balancing speed and accuracy.
Liquid Model Loading:
Addresses the efficiency of delivering AI models to users by storing only selected parts of the models on satellites, with the ability to transfer them between satellites, thus reducing load times and improving spectral efficiency.
Space Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite the vast potential, deploying AI in space faces complex challenges, the most significant being harsh radiation, limited and intermittent power.
For this reason, researchers emphasize the importance of developing radiation-resistant hardware and fault-tolerant computing systems, alongside intelligent task scheduling that considers energy consumption.
The study also outlined future research pathways, including energy-efficient, low-latency, and secure liquid AI, aiming to achieve a balance between performance, reliability, and security.
By relying on predicted satellite orbits and their recurring motion, this model could become the cornerstone for delivering global edge AI in the 6G era.
In this way, satellites are no longer just communication tools; they transform into smart nodes capable of operating AI from the heart of orbit.
Scientists Attempt to "Intercept Cancer" Before Its Formation.. Know the Details

American Fact-Checking Platform Exposes Trump's Exaggerations in State of the Union Addres...

How Mourinho Deceived Everyone and Watched the Match Between Real Madrid and Benfica from...

Fat Loss Improves Blood Pressure and Supports Immunity

Galaxy S26 Armed with a Smart Feature to Combat the Most Dangerous Threats to Smartphones
Discovery of Microplastic Particles in 90% of Prostate Cancer Cases

Artificial Intelligence Diagnoses Children's Brain Tumors with 92% Accuracy Without Surger...

